In certain academic and business situations, it is more valuable to deliver a group presentation than a solo one. Many people prefer group presentations because there is less pressure on the individual. However there are also unique challenges, such as having to ensure multiple individuals collaborate in order to produce a cohesive piece of work.
Preparing for the group presentation
As with any presentation, there is a significant amount of work during the preparation stage. The group must be well organised because there are multiple individuals, and therefore multiple personalities involved.
Presentation moderator
To assist with organisation, the group should first decide on a presentation moderator – this is essentially the “leader”. The presentation moderator can have the final say when decision-making is needed and, during the Q&A portion of the presentation, can decide which speakers will answer certain questions.
Understanding the audience
To make your presentation engaging you need to think about the audience so you can tailor it towards their needs. How much will the audience already know about this topic? What will they want to get from this presentation?
For example, if you are presenting the topic of building a bridge to a group of civil engineers, you can confidently use technical language. However, if you are presenting to secondary school students, you would need to use simpler language and not explain the methods in as much detail.
The presentation’s purpose
As a group, ensure you agree on the purpose of the presentation so that you all understand the message that needs to be conveyed e.g. “We want to find out which treatment works best for social anxiety.” Deciding on your message means that the group can start building key points around this – just keep in mind that each subtopic must contribute to the presentation’s aim.
Divide the presentation
The presentation needs to be divided into main areas so there is a clear beginning, middle and end. This is where can you decide on the order of the subtopics. Presentations usually follow this structure:
1. Introduction:
- It is useful to agree on the first minute of the presentation as a team. This is because the audience should be interested from the start and convinced to listen.
- The presentation’s aims are also discussed and an overview of the presentation’s structure is provided. For example, “We set out to explore the effectiveness of different treatments for social anxiety. We will first cover the symptoms and prevalence of social anxiety, before explaining the different treatments. This will then lead into a discussion about the pros and cons of each treatment route. Finally, we will explain which treatment route we decided was the most effective for this disorder.”
2. One or two middle sections:
- These sections consist of providing the information that addresses your presentation’s aim.
- There can be more of these sections depending on your topic.
3. Conclusion:
- After summarising all of the key points, there must be a clear conclusion. It is beneficial to appoint the conclusion to the best speaker as this is where all the information is pooled together.
After segmenting the presentation, a time sequence can be created so the group understands the order in which tasks must be completed. It is important to set deadlines for this.
Share responsibility
A frequent problem when working within a group is unequal participation as this can subsequently cause disharmony.
But this is easily avoidable by assigning each speaker a section of the presentation to work on depending on their interests. This means that each speaker should be doing the research for their section and putting together a speech and slides (if being used).
Tips:
- It is important to specify exactly what each group member should be doing with their time.
- Make sure the length of time per speaker is agreed on.
- Do not change speakers more than necessary because this can reduce the coherency of the presentation.
Build the presentation together
For an audience to follow and enjoy a presentation, it must flow together. Meeting up and building the presentation helps with this because:
- This prevents the duplication of content.
- You can put the slides together, although only one individual should be responsible for merging the slides so there is consistency within the presentation.
- It is useful to receive feedback on the speeches before presenting to an audience.
- The team can agree on any edits.
- The team can agree on the conclusion.
- You can make sure that each speaker will talk for the same amount of time and cover a similar amount of information.
- The team can come up with the first minute of the presentation together.

Use stories to engage the audience
A good presentation opening could start with a story to highlight why your topic is significant. For example, if the topic is on the benefits of pets on physical and psychological health, you could present a story or a study about an individual whose quality of life significantly improved after being given a dog.
The audience is more likely to remember this story than a list of facts and statistics so try and incorporate relevant stories into presentations.
Know what each speaker will say
Each speaker must know what the other group members will say as this prevents repetition and it may be useful to refer to a previous speaker to assist in explaining your own section.
Also, if a team member is unable to attend on the day it will be easier to find cover within the group.
Write and practice transitions
Clean transitioning between speakers can also assist in producing a presentation that flows well. One way of doing this is:
- Briefly recap on what you covered in your section: “So that was a brief introduction on what social anxiety is and how it can affect somebody”
- Introduce the next speaker in the team and explain what they will discuss: “Now Sarah will talk about the prevalence of social anxiety.”
- Then end by looking at the next speaker, gesturing towards them and saying their name: “Sarah”.
- The next speaker should acknowledge this with a quick: “Thank you Nick.”
From this example you can see how the different sections of the presentations link which makes it easier for the audience to follow and remain engaged.
Practice the presentation
Rehearse with the group multiple times to make sure:
- The structure works
- Everyone is sticking to their timing.
- To see if any edits are needed.
The more you rehearse a presentation the more you will feel comfortable presenting the material and answering questions as your familiarity with the content increases.
Handling nerves before the presentation
It is natural to feel nervous when presenting in front of others, regardless of the size of the audience. Here are some tips:
- Remind yourself that the audience is there to listen to you and wants you to do well; there is no need to be afraid of them.
- Remember that the audience members will have to present their projects later and are almost certainly feeling just as nervous.
- Practicing with your group and practicing your section at home will make you more comfortable and familiar with the material and increase your confidence.
- Practice pauses – when people feel nervous they tend to find silences uncomfortable and try to fill gaps, such as using “um” multiple times (filler words). Practicing pauses will help the silences feel less unnatural when you present therefore reducing the need for filler words.
- When we are nervous we often begin breathing quickly and this in turn can increase our anxiety. Controlled breathing is a common technique that helps slow down your breathing to normal thus reducing your anxiety.
Exercises to control your breathing:
- Sit down in an upright position as it easier for your lungs to fill with air
- Breathe in through your nose and into your abdomen for four seconds
- Hold this breathe for two seconds
- Breathe out through your nose for six seconds
- Wait a few seconds before inhaling and repeating the cycle
During the group presentation
Introducing the team
The presentation should begin with the presentation moderator introducing the team. This is smoother than each individual presenting themselves.
Pay attention to the presentation
You may feel nervous as you wait for your turn to speak but try to listen to the presentation. The audience is able to see the whole team so it is important that you look interested in what is being said and react to it, even if you have heard it multiple times.
Body language and eye contact
Body language is a useful tool to engage the audience:
- If it is your turn to speak then stand slightly in the foreground of the rest of your group.
- Smile at the audience as this will make you look more confident.
- Make eye contact as this helps you engage with the audience.
- Keep your arms uncrossed so your body language is more open.
- Do not look down and read from your notes- glancing down occasionally is fine but keep in mind that you are talking to the audience.
- This is the same for presenting visual aids; you may need to glance at the computer slide but make sure you predominantly face the audience as you are still speaking to them.
- Keep your hands at your sides but use them occasionally to gesture.
Vocal variety
How you say something is just as is important as the content of your speech – arguably, more so. For example, if an individual presented on a topic very enthusiastically the audience would probably enjoy this compared to someone who covered more points but mumbled into their notes.
Here are some pointers:
- Adapt your voice depending on what are you saying- if you want to highlight something then raise your voice or lower your voice for intensity.
- Avoid speaking in monotone.
- Sound enthusiastic – the more you sound like you care about the topic, the more the audience will listen.
- Speak loudly and clearly.
- If you notice that you are speaking quickly, pause and slow down.
- Warm up your voice before a speech
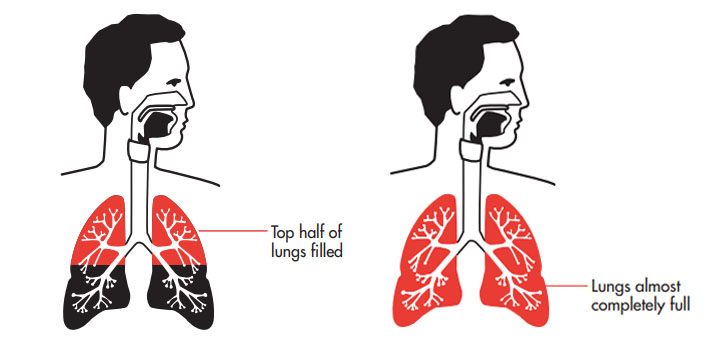
Take short pauses and breath deeply. This will ensure you have more vocal variety.
Handling nerves during the presentation
- If you find that you are too uncomfortable to give audience members direct eye contact, a helpful technique is to look directly over the heads of the audience as this gives the impression of eye contact.
- Try not to engage in nervous behaviours e.g. shifting your weight or fidgeting.
- Remember that it’s unlikely that the audience knows that you are feeling nervous – you do not look as anxious as you feel.
- Notice whether you are speaking too quickly as this tends to happen when nervousness increases. If you are, pause and then slow down.
Strong conclusion
Since the conclusion is the last section of your presentation the audience is more likely to remember it. Summarise the key points and lead into a clear concluding statement. For example, if your presentation was on the impact of social media on self-esteem you could list all the main points covered in the presentation and conclude “Therefore, from the amount of evidence and also from the quality of evidence, we have decided that social media is negatively/positively impacting self-esteem.”
Questions and answer session
The questions and answers session after the main presentation can be a source of anxiety as it is often difficult to predict what questions will be asked. But working within a group setting means that individually you do not have to know everything about the topic.
When an audience member asks a question, the presentation moderator can refer a speaker who has the relevant knowledge to provide an answer. This avoids any hesitant pauses.
If you are answering group presentation questions:
- Pause before answering- take the time to gather your thoughts and think about your answer
- Make sure you answer the question- sometimes you may start providing more information than necessary. Keeping answers as concise as possible will help with this.
- Ask the questioner for clarification if you do not understand- it’s better to ask rather than answering in a way that does not address the question.
- You’re not expected to know everything- challenging questions will emerge and if you do not know the answer you can respond with: “That’s a really good question, I’m not certain so let me look into that.”
Ending the presentation
A good ending usually consists of the presentation moderator thanking the audience. If there is another group afterwards they should transition to the next group.




